Regeneration of ion exchange resin is a process that restores the resin's ability to exchange ions by removing contaminant ions and replacing them with ions from a regenerant solution. This process is necessary when the resin becomes exhausted, meaning that it can no longer facilitate ion exchange reactions.
1. Ion Exchange Resin Regeneration Process
A chemical regenerant solution, such as an acid, salt, or caustic solution, is applied to the resin. The type of regenerant used depends on the resin type and application.
The resin releases contaminant ions and swaps them for ions from the regenerant solution.
The resin is rinsed to remove any remaining regenerant. This is done in two stages: a slow rinse to continue conversion and remove regenerant, and a fast rinse with raw water to ensure water quality.
After rinsing, the resin is ready to be used again.
2. Ion Exchange Regeneration Material
Each resin type calls for a narrow set of potential chemical regenerants. Here, we have outlined common regenerant solutions by resin type, and summarized alternatives where applicable.
-
Strong Acid Cation (SAC) Regenerants
SAC resins can only be regenerated with strong acids. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is the most common regenerant for softening applications, as it is relatively cheap and readily available. Potassium chloride (KCl) a common alternative to NaCl when sodium is undesirable in treated solution, while ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is often substituted for hot condensate softening applications.
-
Weak Acid Cation (WAC) Regenerants
HCl is the safest, most effective regenerant for dealkalization applications. H2SO4 can be used as an alternative to HCl, though it must be kept in low concentration to avoid calcium sulphate precipitation. Other alternatives include weak acids, like acetic acid (CH3COOH) or citric acid, which are also sometimes used to regenerate WAC resins.
-
Strong Base Anion (SBA) Regenerants
SBA resins can only be regenerated with strong bases. Caustic soda (NaOH) is almost always used as an SBA regenerant for demineralization. Caustic potash can also be used, though it is expensive.
-
Weak Base Anion (WBA) Resins
NaOH almost always used for WBA regeneration, though weaker alkalis can also be used, such as Ammonia (NH3), Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), or lime suspensions.
3. How to Regenerate Ion Exchange Resin
Ion exchange resin can be regenerated through a process that includes backwashing, chemical injection, and rinsing. The resin's capacity can be restored by using a high concentration of salt or other regenerant chemical.
Here are some ways to regenerate ion exchange resin:
This process removes suspended solids and redistributes compacted resin beads.
A high concentration of salt or other regenerant chemical can be used to restore the resin's capacity.
A 4% concentration of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can be used to regenerate anion resin.
This can be used to regenerate anion resin and return it to the chloride form.
This can be used to sterilize resin and clean the resin bed. However, hydrogen peroxide can decompose if iron fouling or other metals are present.
-
Ammonium Bicarbonate Solution
A combination of heat and pre-washing with this solution can completely regenerate the resin.
2. Characteristics of Ion Exchange Resin
Whether or not ion exchange resin is hazardous depends on several factors, including:
The type of resin: Some resins contain potentially harmful chemicals, while others are relatively inert.
The form of the resin: Dry resin can be dusty and irritating to the eyes and skin, while wet resin may not pose the same risks.
The presence of contaminants: If the resin has been used to remove contaminants from water or other liquids, it may be contaminated with those substances. These contaminants could be hazardous, depending on their nature.
Ion exchange resins have many advantages, including:
● Cost
Ion exchange resins can be economical, with costs about half those of traditional methods like bone char or granular carbon.
● Equipment Size
Ion exchange resins require less bulky equipment than other materials, as they have a greater flow rate.
● Automation
The resin process can be easily automated, and the liquor and adsorbent are contained in a closed vessel, making it more hygienic than other decolorization processes.
● Regeneration
Ion exchange resins can be regenerated by washing them with a concentrated solution of the desired ion, unlike other filtration methods that generate waste.
● Lifespan
Ion exchange resins can have lifespans of at least six years, and potentially longer than 12 years.
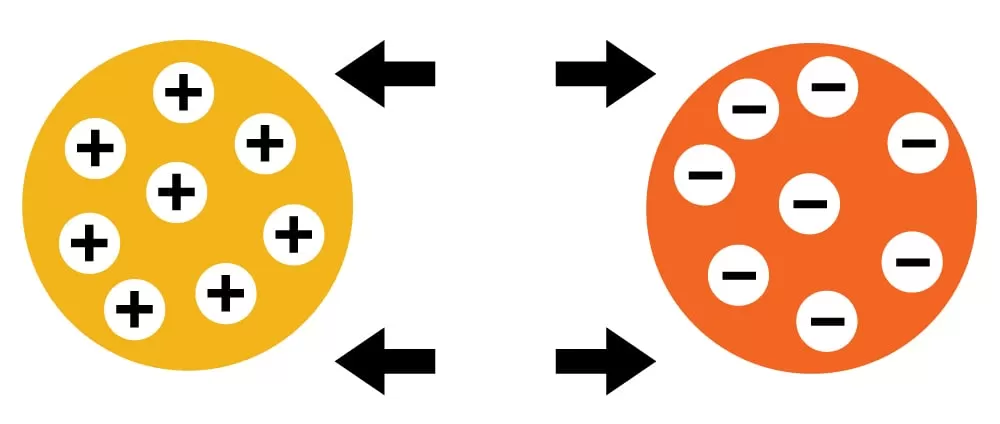
The main difference between cation and anion exchange is the charge of the ions they exchange:
Cation exchange: Exchanges positively charged ions, or cations.
Anion exchange: Exchanges negatively charged ions, or anions.
Here are some other differences between cation and anion exchange:
● Resins
Cation and anion exchange resins are small, porous plastic beads with a specific charge. They are chemically similar and are both polymers.
● Applications
Cation and anion exchange resins are used in industrial water purification and separation. For example, a strong anion exchange column can remove negatively charged DNA or endotoxins.
● Soil
Cation exchange capacity (CEC) is the amount of negative charge available to attract cations in soil. Anion exchange capacity (AEC) is the amount of positive charge available to attract anions in soil. In most soils, CEC is greater than AEC.
● Amphoteric exchangers
Some exchangers can exchange both cations and anions simultaneously.
Physical factors:
Resin type: Different resins have specific functional groups and pore structures that determine their selectivity for certain ions.
Particle size: Smaller particles offer higher surface area for ion exchange but increase pressure drop within the system. Larger particles have lower pressure drops but slower exchange kinetics.
Density: Density affects resin bed expansion and backwashing behavior.
Chemical factors:
pH: The solution's pH significantly impacts the ionization state of target ions and the resin's functional groups.
Ionic strength: Higher ionic strength in the solution can compete with target ions for exchange sites, reducing resin capacity.
Presence of complexing agents: Complexing agents can bind target ions, making them unavailable for exchange with the resin, thus reducing efficiency.
Temperature: Elevated temperatures generally increase exchange kinetics but can also degrade the resin and accelerate leaching of functional groups.
Operational factors:
Flow rate: Higher flow rates reduce contact time between ions and the resin, potentially affecting exchange efficiency. However, excessively low flow rates can lead to channeling and inefficient bed utilization.
Loading rate: Applying excessive feed loads can overwhelm the resin's capacity and lead to breakthrough, where target ions start appearing in the effluent.
Regeneration process: The type and concentration of regenerant used, as well as the regeneration flow rate and duration, can impact the efficiency of removing captured ions and restoring the resin's capacity.
Ion exchange capacity (IEC) is a measure of a material's ability to displace ions that are already attached to it. It can refer to the capacity of a membrane or soil to exchange ions:
● Membranes
IEC is a measure of the concentration of ion-conducting functional groups in a membrane. It's expressed as milliequivalents per gram of the membrane. IEC is a key property of anion-exchange membranes (AEMs) and is related to other AEM properties, such as anion conductivity and water uptake.
● Soil
IEC is a fundamental property of soil that affects soil fertility and the exchange of ions in the soil. Soil particles have negative charges that attract positively charged ions, such as potassium, magnesium, and ammonium. The amount of nutrients that can be attached to soil particles increases with the CEC.
IEC is also a measure of the number of positive or negative charges that an exchange resin can bind to. It's reported in singly charged ion equivalents per gram of resin.
An ion exchange column is a chromatography column that separates compounds based on their charge. They are used in a variety of applications, including:
● Biochemistry: Ion exchange columns are used to purify and isolate proteins and nucleic acids.
● Water Softening: Ion exchange columns can be used to soften water by removing calcium and magnesium ions.
● Biopharmaceutical Production: Ion exchange columns are used in the production of biopharmaceuticals.
● Clinical Diagnostics: Ion exchange columns are used in clinical diagnostics.
● Quality Control: Ion exchange columns are used in quality control.
There are two types of ion exchange columns: cation exchange and anion exchange:
● Cation Exchange Columns
These columns have a negative charge and capture positively charged molecules.
● Anion Exchange Columns
These columns have a positive charge and capture negatively charged biomolecules.

Water softener resin is a material used in water softeners to remove minerals that make water hard. It's made of small beads that are packed in a bed inside the water softener tank. The resin beads are coated with sodium ions, which have a positive charge. When hard water flows through the resin bed, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water are attracted to the resin beads and replace the sodium ions. The softened water then exits the water softener.

Here are some things to know about water softener resin:
● Composition
Water softener resin is made from synthetic materials, such as polystyrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The beads are porous and skeletal, and range in size from 0.3–1.2 mm.
● Lifespan
Depending on the type of resin and how well the water softener is designed, resin beads can last between 5–20 years. However, they may need to be replaced more frequently if the water is very hard or if the city uses strong chemicals to treat water contamination.
● Hydraulic Shock
When water is turned off quickly, it can create a shock wave that travels back through the plumbing system and cracks the resin beads. This is known as hydraulic shock, or "water hammer".
● Fine Mesh Resin
Fine mesh resin is smaller than regular resin, so it can fit more beads into a smaller space.
Ion chromatography (or ion-exchange chromatography) is a form of chromatography that separates ions and ionizable polar molecules based on their affinity to the ion exchanger. It works on almost any kind of charged molecule—including small inorganic anions, large proteins, small nucleotides, and amino acids. However, ion chromatography must be done in conditions that are one pH unit away from the isoelectric point of a protein.
One of the primary advantages for the use of ion chromatography is that only one interaction is involved the separation, as opposed to other separation techniques; therefore, ion chromatography may have higher matrix tolerance. Another advantage of ion exchange is the predictability of elution patterns (based on the presence of the ionizable group).
The global ion exchange resins market size was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 2.2 billion by 2025, growing at 4.2% cagr from 2020 to 2025. Urbanization in APAC and increasing demand for nuclear energy are some of the key factors driving the market.
Ion exchange in chemistry is a process where ions are exchanged between a solution and an ion exchange material. This material can be a synthetic resin or a naturally occurring substance like zeolite. The process is reversible, allowing the ion exchange material to be regenerated for repeated use.
Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:
1. Ion Exchange Material: This is usually a solid substance that contains ions which can be exchanged. It can be a resin with charged sites that attract ions of the opposite charge.
2. Exchange Process: When a solution containing different ions comes into contact with the ion exchange material, ions from the solution are swapped with ions from the material.
3. Cation and Anion Exchangers: There are two main types of ion exchangers—cation exchangers, which exchange positively charged ions (cations), and anion exchangers, which exchange negatively charged ions (anions).
4. Applications: Ion exchange is widely used for water softening, purification of chemicals, and separation of substances. It’s also used in scientific laboratories for purifying and analyzing mixtures, and in medical applications like artificial kidneys.
The process is governed by the selectivity of the ion exchange material, which is influenced by the size, charge, and structure of the ions involved. For example, common ions that can bind to ion exchangers include
H+
(proton) and
OH−
(hydroxide), as well as various monovalent and divalent ions.
3. What Will Ion Exchange Remove?
Yes, ion exchange resin can be effective in removing fluoride from water. However, its effectiveness depends on several factors:
Type of resin:
Strong base anion exchange resins: These are the most common type used for fluoride removal.
Specific fluoride adsorbents: These resins are designed specifically for fluoride removal and are often made with highly selective materials like activated alumina or lanthanum oxide.
Water chemistry:
pH: The efficiency of ion exchange resins decreases at higher pH levels.
Other anions: The presence of other negatively charged ions, such as sulfate and nitrate, can compete with fluoride for the exchange sites, reducing the amount of fluoride that can be removed.
Fluoride concentration: The effectiveness of the resin is also affected by the initial concentration of fluoride in the water. Lower concentrations are generally easier to remove.
Sunresin Technology is at the forefront of wastewater treatment innovation with its advanced ion exchange method. This method is key to their Ammonia Nitrogen Removal Process, which is tailored to remove ammonia from evaporative condensate water—a frequent byproduct in various industrial evaporator units.
Evaporators, which turn liquid into gas, produce evaporative condensate water when water and steam mix and then condense back into water. As evaporation concentrates the mother liquor, ammonia nitrogen, due to its volatility, vaporizes and then liquefies upon cooling. The form of ammonia nitrogen in water depends on the pH: above 9, it's NH3; below 9, it’s mostly NH4+. Addressing ammonia nitrogen in evaporative condensate water is a widespread industrial challenge.
The stripping method, which involves air contact, is ineffective for low-concentration ammonia nitrogen due to its solubility. It's suitable for high-concentration wastewater but not for evaporative condensate water. The biochemical method, involving nitrification and denitrification, is energy-intensive and costly. Chemical precipitation, which forms ammonium magnesium phosphate precipitate, is also costly and less used domestically.
The Ion Exchange Method offers a solution for deep ammonia nitrogen removal from evaporative condensate water, overcoming issues like difficulty in treating low concentrations and high operational costs. It's efficient, non-toxic, requires minimal space, and doesn’t need infrastructure. The process also allows the high-concentration regeneration liquid to be returned to the MVR evaporation system.
In water, ammonia forms hydrated ammonia and ionizes into NH4+ and OH- below pH 9. The Seplite® XDA series ammonia adsorption resin, used in this process, favors the resin’s selective adsorption of ammonia when in the form of ammonium salt.
The Seplite® XDA Series resins are used extensively in the chemical industry for refining and wastewater treatment. Developed by Sunresin, these resins have a high exchange capacity and long service life, making them suitable for treating wastewater from dye, pesticide, pharmaceutical, and intermediate production. They can also recover phenols, amines, organic acids, nitro compounds, and halogenated hydrocarbons.
The working principle involves ion exchange, where wastewater passes through the resin bed, and ammonia substances are exchanged onto the resin, purifying the water. Desorption allows for resin reuse, with dilute alkali for acidic solutes, dilute acid for basic solutes, and organic solvents or steam for neutral solutes, depending on the boiling point.
Cation resin is commonly used for water softening applications to remove hardness-causing minerals like calcium and magnesium. By removing these minerals, the water becomes less likely to form soap scum and scale buildup in pipes and appliances.
Here are some other applications of cation resin:
1. Purification: Cation resin can be used to remove contaminants like lead, copper, and mercury from drinking water or industrial wastewater.
2. Food and Beverage Industry: In the food and beverage industry, cation resin can be used to adjust acidity levels, remove minerals that affect taste or color, and improve the clarity of juices and other beverages.
3. Chemical Production: Cation resin is used in various chemical production processes to purify chemicals and remove unwanted ions.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, cation resin is used to purify drugs and remove contaminants.
Anion resin targets negatively charged ions, also known as anions, dissolved in water. There are two main types of anion resins used in various applications:
1. Strong base anion (SBA) resins: These are typically used for demineralization, dealkalization, and desilication. They can also remove total organic carbon (TOC) or other organics depending on the specific resin. Some of the common anions removed by SBA resins include:
● Sulfates
● Nitrates
● Arsenic
● Silica
● Fluoride
2. Weak base anion (WBA) resins: These are often used in conjunction with SBA units for demineralization applications. They primarily target anions associated with stronger acids, such as:
● Chloride
● Sulfate
Anion exchange is a widely used process in water treatment for various purposes, including:
● Demineralization: This process removes almost all inorganic salts present in water. SBA resins are particularly effective in demineralization by capturing a broad range of anions.
● Dealkalization: This process reduces the alkalinity of water, which is especially important in boiler feedwater treatment. SBA resins can remove carbonate and bicarbonate ions that contribute to alkalinity.
● Desilication: SBA resins are adept at removing silica from water, which is crucial in various industrial applications where silica buildup can be detrimental.
● Organic removal: Certain SBA resins can also target organic contaminants in water.
The Ion Exchange Resin Method is a water treatment process that removes hardness-causing ions, such as calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺), from water. Here’s how it works:
1. Water Softening: This is the most common ion exchange process, which specifically targets the reduction of calcium and magnesium in the water.
2. Ion Exchange Resins: These are microporous beads made from materials like polyacrylate and polystyrene, which range from 0.3 to 1.3 millimeters in size. As water passes through these beads, the ions inside the resin interact with the ions present in the water, capturing the contaminants.
3. Cation Exchange: In this step, positively charged ions (cations) in the water are exchanged with other positively charged ions (usually sodium) on the resin surface.
4. Anion Exchange: Similarly, negatively charged ions (anions) are exchanged with other negative ions (usually chloride) on the resin surface. This is important for removing contaminants like nitrate, arsenic, sulfate, and fluoride.
Ion exchange resins are used in water treatment to remove undesirable ionic contaminants from water by exchanging them with another ionic substance. The process involves passing water through a column containing ion exchange resin, which attracts and binds the contaminants while releasing a different, less problematic ion into the water.
Here's a breakdown of the function of ion exchange resin in water treatment:
1. Water Softening: This is the most common use of ion exchange resins, where calcium and magnesium ions, which cause water hardness, are replaced with sodium ions.
2. Deionization: It removes nearly all ionized minerals and salts from the water, producing highly purified water.
3. Demineralization: Similar to deionization, it removes all cations and anions from the water, but it uses both cation and anion exchange resins.
4. Dealkalization: It reduces the alkalinity of water, which is important for preventing scale formation and corrosion in water systems.
An ion exchange water treatment system is a specialized technology used in wastewater treatment to remove dissolved ions and contaminants from water. This system relies on ion exchange resins that attract undesirable ions in the wastewater and exchange them with more desirable ions, effectively purifying the water before discharge. Ion exchange water treatment systems play a significant role in wastewater treatment and contribute to improving water quality and meeting various industrial and domestic needs.
All natural waters contain, in various concentrations, dissolved salts which dissociate in water to form charged ions. Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions are called anions. Ionic impurities can seriously affect the reliability and operating efficiency of a boiler or process system. Overheating caused by the buildup of scale or deposits formed by these impurities can lead to catastrophic tube failures, costly production losses, and unscheduled downtime.
Hardness ions, such as calcium and magnesium, must be removed from the water supply before it can be used as boiler feedwater. For high-pressure boiler feedwater systems and many process systems, nearly complete removal of all ions, including carbon dioxide and silica, is required. Ion exchange systems are used for efficient removal of dissolved ions from water.
The ion exchange process for water softening has several advantages, making it a popular choice for treating water. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Rapid Results: Ion exchange can quickly remove inorganic ions from water, providing immediate improvements in water quality.
2. High Effectiveness: It is very effective at removing hardness-causing ions such as calcium and magnesium, as well as other inorganic ions.
3. Versatility: Suitable for both short-term and long-term applications, ion exchange systems can be tailored to meet specific water treatment needs.
4. Ease of Installation: These systems can be quickly installed, ensuring minimal disruption to existing operations.
5. Low Maintenance: Once installed, ion exchange systems require relatively little maintenance, which can reduce long-term operational costs.
6. Regeneration Capability: The resin used in the ion exchange process can be regenerated, allowing for repeated use and reducing waste.
7. Cost-Effective: The initial investment for an ion exchange water softening system is relatively inexpensive compared to other treatment methods.
These advantages contribute to the widespread use of ion exchange in various water treatment applications, from industrial processes to domestic water softening. It’s a reliable method to ensure that water is softened and suitable for use without the negative effects of hard water.
The main areas of the food industry where the ion-exchange process is currently used are: sugar, dairy products and water purification. It is also used to recover, sepa- rate and purify biochemicals and enzymes, and is currently being introduced to the drinks industry for juices and wines.
There are many ways to finish the processing of food raw materials. The ion exchange and adsorption resins are often used in the later finishing process due to their good selectivity and high processing precision, since it provides an effective and safe path for improving the quality of food ingredients, which could remove the deeper color of the food, remove the odor, remove the pesticide residue, and even make it more comfortable taste.
More than a decade ago, China's juice industry faced severe challenges because pesticides were used in apple cultivation. Although the fruits were strictly cleaned, the final juices were still exceeding the standard for pesticides. The Chinese juice manufacturing industry was facing the risk of shutting down. At that time, Sunresin started the research on juice purification technology, and first introduced the juice resin for removing pesticide residues, and introduced the whole process very quickly. Nowadays Chinese juice makers are all benefiting from Sunresin's technology.

Sunresin was also become into the first provider applying the resin adsorbent techniques in food processing. Up to now in the Chinese market, the adsorbent techniques applied in juice industries all originate from Sunresin initiation. After nearly 20 years of continuously technical innovation and industrialization in this field, new resins and solutions specialized for food processing have stood firmly in the market, which are separately specified for nutrition products, fruit juices such as apple, orange, pear, pineapple, lemon, grape and pomegranate, as well as in sugar industries. More than 5000M3 of the these products have been supplied to beverage industry of both domestic and overseas with over tens of production lines scoping from 5t/hr to 100t/hr.
Sunresin provides a well-established ion exchange resin process for acetic acid purification, which can remove bromine or chloride ions in acetic acid to less than 5ppm, or undetectable levels. The fixed bed mode is recommended for the ion exchange process for acetic acid purification, which runs continuously and removes impurities through the front and back resin columns to improve the removal accuracy and ensure the maximum utilization of the resins.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ion exchange resin is a versatile and effective material that can perform various functions in different fields. We have answered 30 frequently asked questions about ion exchange resin, hoping to provide you with some useful information and guidance.
If you want to learn more about ion exchange resin, you can visit the website of Sunresin, a leading manufacturer of ion exchange resin in China. Sunrise offers high-quality and customized ion exchange resin products for various needs and purposes. You can also contact Sunrise for professional advice and service.