A Better Choice for Tungsten and Molybdenum Separation
Tungsten is a non-ferrous metal with high hardness, high melting point, high temperature strength and good corrosion resistance to molten alkali metals and steam. It is mainly used in the manufacture of filaments, high-speed cutting alloy steels, and hard molds. Because of its high melting point, tungsten is generally refined by hydrometallurgical process. The schematic diagram of the refining process is as follows:
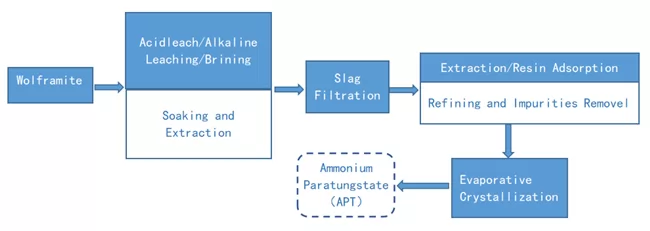
However, tungsten ore is often associated with varying amounts of molybdenum. Tungsten and molybdenum are elements of the same group and have similar physical and chemical properties. It is difficult to separate tungstate and molybdate. Therefore, in the smelting and extraction process of tungstate, the extract effective separation of tungsten and molybdenum is the difficulty and key of the whole process.
For tungsten ores with low molybdenum content (such as wolframite, the molybdenum content is generally less than 0.04%), the crystallization rate can be controlled through the evaporation crystallization link, so that 80%-90% of the molybdenum remains in the crystallization mother liquor to achieve separation of tungsten and molybdenum. For tungsten ores with high molybdenum content (such as molybdenum-containing scheelite), it is difficult to simply control the crystallization rate through evaporation and crystallization because of the high content of molybdenum in the refined liquid after the use of traditional refined impurity removal materials and processes. To obtain qualified tungstate products under the premise of ensuring the yield, the processing procedures become complicated, and the labor intensity and production cost are significantly increased. With the gradual consumption of high-quality tungsten ore resources, there will be more and more medium and low-quality tungsten ore resources containing more impurities (the molybdenum content in the ore is getting higher and higher). How to choose a more efficient tungsten and molybdenum separation material and technology will become the key technology that affects the development of tungstate extraction and smelting industry.


Aiming at the separation of tungsten and molybdenum in tungstate extraction and smelting, Sunresin has set up special topics and established a special research team based on customers’ needs to conduct research and analysis on the element composition and existing technology of tungsten leaching solution, and successfully developed sepcial resin Seplite® LSC680 for tungsten and molybdenum separation as well as the matching process. Through special pretreatment to the feed solution, the molybdenum in the solution will be highly selectively adsorbed on the LSC680 resin, while the tungsten remains in the solution after adsorption. The separation of tungsten and molybdenum can be realized in a simple and efficient manner.

Tungsten and Molybdenum separation data by using Seplite® LSC680 resin:
| Tungsten content (g/L) | Mo content (g/L) | Mo-W ratio | Mo removal rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 250 | 2.5 | 1:100 | >98.5 |
| After | >245 | <0.03 | 1:10000 |
Note: All relevant data comes from customers feedback on site.
The advantages of seplite® LSC680 resin:
(1) Good adaptability, suitable for ammonium salt, sodium salt, high molybdenum and low molybdenum feed liquid.
(2) Simple process and easy operation, without bringing in foreign impurities.
(3) Excellent separation effect of Tungsten and Molybdenum, and the Mo-W ratio in the effluent liquid is low, which can meet the requirements of 0-level APT products.
(4) High treatment capacity.
(5) Easy to be desorbed and regenerated with multi-cycle use.















