Application of Chromatography Technology in Synthetic Biology
In the field of synthetic biology, chromatography separation technology is commonly used for the purification and production of synthetic products, as well as for isolating metabolites and identifying the structure and characteristics of compounds and biomolecules. It is also widely applied in the field of adsorption and separation.
1. Chromatography separation technology:
Principle: Moving fast.
A fluid phase (gas, liquid, or supercritical fluid) containing a sample flows over a stationary phase surface that is fixed to a column or a plate and is immiscible with the fluid phase. During the separation process, as the sample components pass through the stationary phase, the components with stronger interactions with the stationary phase are eluted more slowly with the flow of the fluid phase, while the components with weaker interactions with the stationary phase are eluted more quickly with the flow of the fluid phase.Due to the difference in elution speed, the mixed components eventually form individual "bands" or "zones" of each single component, and each single component substance that elutes sequentially can be collected separately, thereby achieving the separation of the components.
_1698303308_WNo_600d510.webp)
Image: processing of chromatography separation and resin position inside the chromatographic column
2. The Impact of Column Length on Chromatography Plants:
In a chromatographic separation plant, the column length can have a significant impact on the separation performance.When using the same resin, feedstock, and adsorbability, a longer column can result in better separation efficiency and higher product concentration.
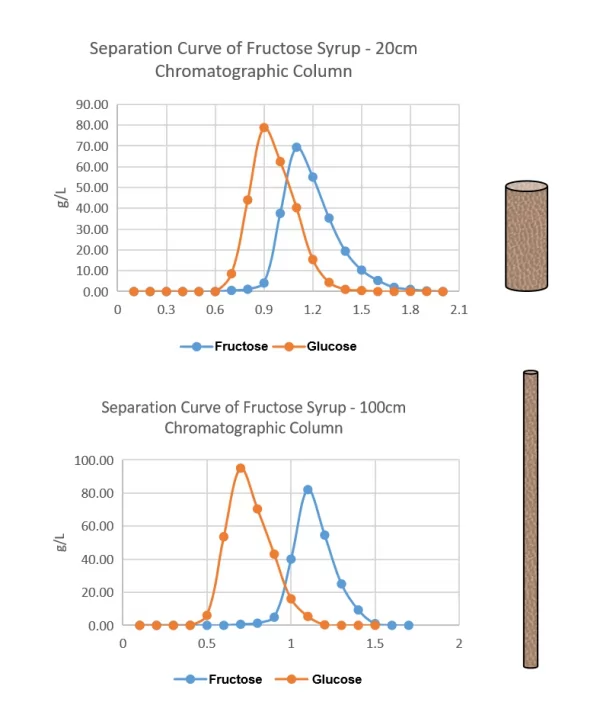
For example, Sunresin's fructose and glucose chromatography equipment can achieve a product concentration of 80g/L with a shorter column length of 20cm, while a longer column length of 100cm can increase the product concentration to 100g/L.
When selecting a chromatographic column for industrial applications, factors such as the separation process, resin particle diameter, operating pressure, and other considerations should be taken into account.
3. The Selection of resin for chomatographic seperation equipment:
| Number | Type | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Monojet S1850 | Gel | Starch sugar,sugar alcohol,amino acid |
| Monojet S2850 | Gel | Separation of organic acids. |
| Monojet S3850 | Gel | Separation of multiple types of amino acids. |
| Monojet S4850 | Gel | Separation of sugar/acids. |
Chromatographic columns typically do not use uniformly sized particles, as this can affect flow resistance, separation efficiency, and repeatability. However, uniform particle resins have great potential for high-level fine separation. These resins are widely used in chromatographic separation equipment due to their high stability and mechanical strength, which results in better separation efficiency and stability. They can provide more accurate and reliable separation results compared to non-uniform particle resins.
4. SSMB Continuous Chromatography Technology Equipment:
1)Working Principle:
Due to the different forces between substances and the stationary phase (packing material), they will flow out of the chromatographic column in order under the action of the eluent (mobile phase), as shown in the diagram.
2)SSMB Technology:
In the simulated moving bed system, the entire adsorption bed layer consists of several interconnected chromatographic columns. The stationary phase in the chromatographic columns no longer undergoes reverse flow movement, and the columns themselves no longer move. Instead, the reverse movement of the stationary phase is simulated through valve switching. The inlet and outlet ports move sequentially along the flow direction of the mobile phase, effectively simulating the reverse movement of the stationary phase and the mobile phase, achieving the purpose of separation.
3)Advantages of the Equipment:
a. High separation accuracy, capable of obtaining highly pure components.
b. It does not consume chemicals, only water, and is more environmentally friendly.
c. The system has good stability and high automation, improving production efficiency.
4)Applications of Continuous Flow Chromatography:
a. Separation and purification of petrochemical products.
b. Separation and purification of proteins, peptides, and amino acids.
c. Separation of sugar alcohols.
d. Terminal purification and refinement of chemical synthesis drugs and biopharmaceuticals.
e. Separation of chiral compounds.
f. Separation and purification of natural product functional components.















