Application of Specialized Ammonia Nitrogen Treatment Resin in Evaporative Condensate Water
Understanding Evaporative Condensate Water
An evaporator is a common device used to convert liquids into gases. Evaporative condensate water is formed in steam generators and heat exchangers when water and steam mix, and then cool and condense back into liquid through heat exchange.
During the evaporation process, as the mother liquor becomes more concentrated in the evaporator, the solution temperature rises. Due to the volatile nature of ammonia nitrogen (NH₃-N), it transitions into a gaseous state along with water vapor. Once cooled, it condenses back into liquid form and remains in the water. When the pH is above 9, ammonia nitrogen exists primarily in the form of NH₃. Below pH 9, it predominantly exists as NH₄⁺ (ammonium ion).
The treatment of ammonia nitrogen in evaporative condensate water is a common challenge for industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing.
Technology for Removing Ammonia Nitrogen from Evaporative Condensate Water
Stripping Method:The stripping method involves bringing wastewater into contact with air, allowing ammonia nitrogen to transfer from the liquid phase to the gas phase due to the difference between the actual concentration in the wastewater and its equilibrium concentration. However, due to the solubility of ammonia nitrogen, it is difficult to further reduce its concentration through stripping alone. The application of stripping for ammonia nitrogen removal from distilled water is ineffective and may even lead to a deterioration in water quality, significantly increasing conductivity. Therefore, this method is more suitable for high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater but is not ideal for treating evaporative condensate water.
Biological Treatment:Biological treatment utilizes the nitrification and denitrification processes of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria to convert ammonia nitrogen in wastewater into nitrate, which is then converted into nitrogen gas and removed. However, this method has several drawbacks, including long process duration, large land requirements, the need for additional carbon sources, high energy consumption, and high operational costs.
Chemical Precipitation Method:The chemical precipitation method removes ammonia nitrogen by adding magnesium compounds and phosphate or phosphate salts to wastewater, causing NH₄⁺, Mg²⁺, and PO₄³⁻ to react and form magnesium ammonium phosphate (MAP) precipitate. However, the high cost of phosphorus and magnesium salts makes this method expensive, limiting its application in China.
Ion Exchange Method for Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Evaporative Condensate Water
The ion exchange method is highly effective for the deep removal of ammonia nitrogen from evaporative condensate water. It offers excellent stability and resolves common issues in existing technologies, such as difficulty in reducing low-concentration ammonia nitrogen, large equipment size, and high operational costs.
Additionally, this method does not introduce toxic or harmful ions into the treated water. It is highly efficient, non-toxic, and safe to use. It requires minimal space and offers the advantage of recovering high-concentration regeneration liquid, which can be returned to the MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) evaporation system for reuse.
Application of SEPLITE® MC Series Ammonia Nitrogen Adsorption Resins
Sunresin produces a wide range of resins that are widely used in the chemical industry, particularly in the refining of organic chemical products and wastewater treatment. With extensive industry experience, Sunresin has developed specialized ammonia nitrogen treatment resins for organic chemical wastewater treatment.
The SEPLITE® MC Series resins are specifically designed by Sunresin for removing ammonia nitrogen from organic chemical production wastewater. These high-capacity ion exchange resins are based on extensive research and development in macroporous and uniform-pore resins. They offer advantages such as high exchange capacity, easy regeneration, and long service life.
These resins are mainly used for treating wastewater from industries such as dyes, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and their intermediates. They can also be applied in the adsorption and recovery of phenols, amines, organic acids, nitro compounds, and halogenated hydrocarbons. The use of SEPLITE® MC Series series resins for treating organic chemical production wastewater provides significant economic and social benefits, with a mature and reliable process.
Working Principle of Ammonia Nitrogen Adsorption Resins
Resin adsorption:During the actual application, ammonia-containing substances in wastewater pass through the resin bed, where they undergo ion exchange and are adsorbed onto the resin, effectively purifying the wastewater.
Desorption:The adsorbed ammonia substances can be completely eluted using an appropriate method, allowing the resin to be reused. Generally, acidic solutes are desorbed using a dilute alkaline solution, basic solutes using a dilute acid solution, and neutral solutes using an organic solvent or steam regeneration based on boiling point selection.
Customer Case: Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Evaporative Condensate Water
Process Flow Diagram
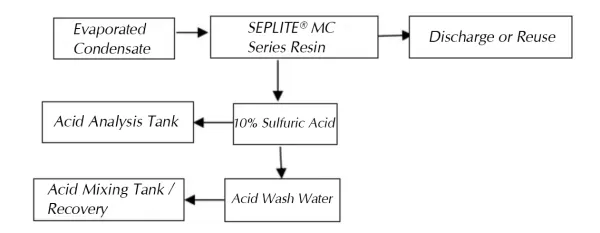
Overall Process
In one client case, the wastewater treatment system was designed for a flow rate of 10 m³/h using a single-column operation mode.
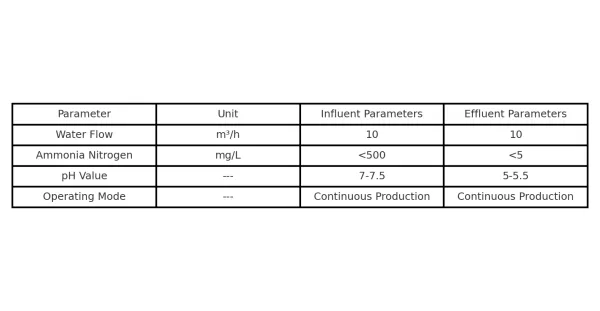
In this project, the designed operation water volume is 10 cubic meters/hour, the influent ammonia nitrogen content is about 500 mg/l, and the PH value is about 7~7.5. After resin process treatment, the effluent ammonia nitrogen content is less than 5 mg/l, and the PH value is about 5~5.5, which fully meets customer requirements.
Free Quote
Resources
Adsorbent Resin
Bio-Pharmaceutical & Life Science
Enzyme Carriers
Hydrometallurgy & Mining
Chelating Resin
Chemical Industry
Chromatographic Media
Wastewater Treatment&Reuse
Food & Beverage Industries
Ion Exchange Resin
Civil & Industry Water Treatment
Equipments And Projects
Plant Extraction
Catalyst Resin
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
Product
Application
Contact Us
Sunresin Park,No.135, jinye Road, Xi’an Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Shaanxi-710076, China
seplite@sunresin.com
seplite_europe@sunresin.com
+86-29-89182091
Our Product List
Latest News
30
2024 08
Sunresin Makes Hurun China Top 500 List
The Hurun Research Institute recently released their "2023 Hurun China Top 500" list, with Sunresin has making the list in recognition of its outstanding market performance and innovation capabilities. This is the only company on the list in China's adsorption separation materials industry.
22
2024 06
Exhibition Highlights | Sunresin Showcases at SIWW 2024 Singapore International Water Week
From June 19-21, 2024, the Singapore International Water Week (SIWW Water Expo 2024) was held at the Marina Bay Sands Expo and Convention Centre in Singapore. Sunresin showcased its internationally leading products and technologies at the event.
10
2024 05
Sunresin and Latin America: Ten thousand miles are still neighbors
In April, Ambassador Xu Yicong's book launch of "Family and Country Sentiments - Continuing Chapter" was successfully held in Beijing. The ambassadors of Latin America in China have come to congratulate Ambassador Xu, and Zhai Feng, Vice President of Bump Cycle, attended to celebrate the event. Dr. Gao Yuejing, as the representative of the important guests, gave a speech and expressed her most sincere blessing to Ambassador Xu for the publication of his new book.
Leave a Message
Please send any questions you want to know, we will reply to you immediately.
Choose File
Submit















